BIM in Construction Leads the Way: 8 Revolutionary Construction Trends For 2026
Introduction
The construction industry is entering a revolutionary phase. With increasing pressure from labor shortages, sustainability targets, and the need for faster project delivery, companies are turning to emerging technologies and smarter workflows to stay competitive.
As we look toward 2026, several transformative trends in BIM in construction are gaining traction and reshaping the way we build, particularly in the context of reinforced concrete structures, rebar detailing, and prefabricated components.
From modular construction to AI-powered tools and real-time BIM integrations, this article explores the most impactful innovations that will define the construction landscape in the coming year.
Modular and Prefabricated Construction is Booming
Modular and prefabricated construction methods have been gaining momentum globally, and 2026 is set to be a breakout year. Market projections show that the modular construction industry will grow from $104 billion in 2024 to $140.8 billion by 2029. A significant acceleration is expected in 2026, driven by increasing demand for cost-effective and fast-paced construction methods.
Modular construction allows for large portions of a building, including structural elements such as precast walls, beams, and even reinforcement cages, to be fabricated offsite in controlled environments. This reduces the impact of weather delays, improves quality control, and significantly cuts down on-site construction time.
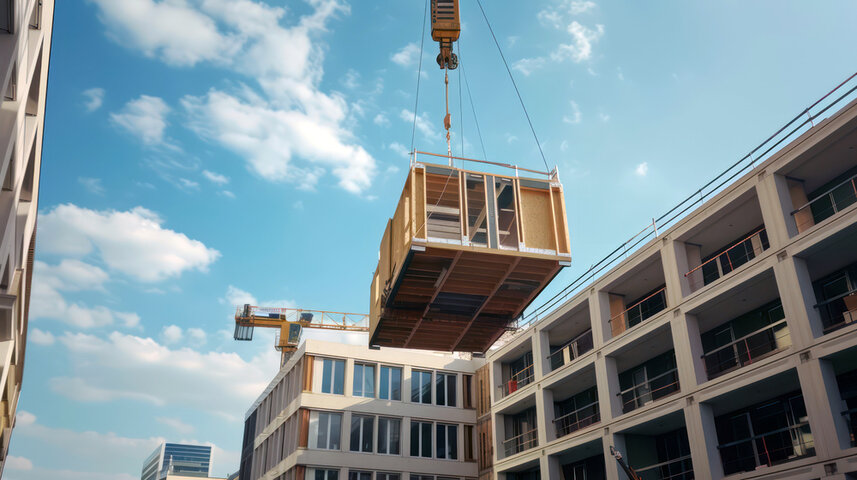

DfMA (Design for Manufacture and Assembly) principles are becoming foundational in this shift, where components like MEP racks and restroom pods are standardized for repeatability and speed. Logistics planning, crane path optimization, and just-in-time sequencing are critical success factors in the adoption of modular workflows.
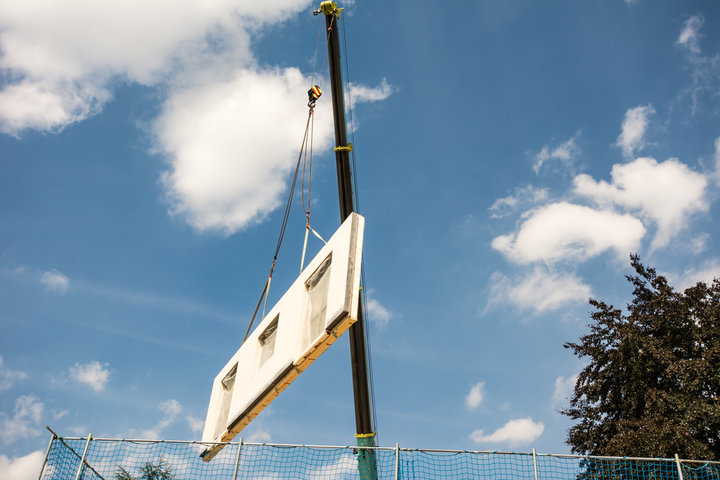

For rebar detailers and structural engineers, BIM in construction presents both a challenge and an opportunity. The need for precise 3D modeling, advanced reinforcement planning, and seamless integration with manufacturing facilities makes Building Information Modeling (BIM) a critical tool in the process. Software platforms like Allplan, Revit, and Tekla are central to enabling this workflow, ensuring that reinforcement drawings are accurate, clash-free, and production-ready.
AI-Powered Tools Tackle Labor Shortages and Inefficiencies
One of the defining challenges in construction today is the persistent shortage of skilled labor. In response, AI in construction is being adopted rapidly across project lifecycles. In 2026, expect to see widespread implementation of AI tools designed to automate time-consuming and labor-intensive tasks.
ADAPT: Autonomously Handling Heavy Lifting
An example of this is ADAPT, an autonomous off-road forklift designed to maneuver through construction sites, transporting and staging materials like rebar bundles, concrete panels, and formwork. With AI-powered navigation and obstacle avoidance, ADAPT reduces reliance on human labor for site logistics, minimizing delays and improving material flow.
BILD AI: Automating Drawing Analysis
Another tool making waves is BILD AI, a platform that analyzes construction drawings using machine learning. It can automatically extract rebar quantities, detect inconsistencies, and estimate material costs. For rebar detailing professionals, this means less time spent on take-offs and more time focused on design optimization and coordination.
AI tools are also being integrated into cost estimation, risk forecasting, and generative layout design, operating behind the scenes to offer predictive suggestions and flag coordination issues. This shift toward background AI support is expected to reduce rework, cut delays, and optimize planning cycles.
Edge AI and Autonomous Drones
AI is no longer confined to desktop environments or cloud-based systems. Edge AI refers to artificial intelligence algorithms processed locally on devices such as drones or cameras. In 2026, this capability will become integral to jobsite monitoring and safety enforcement.
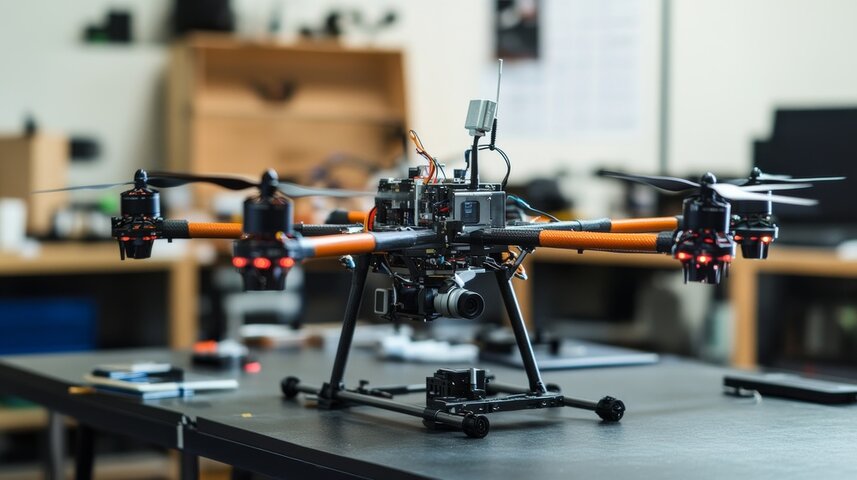

Edge AI drones equipped with computer vision can fly autonomously, capturing data in real time without needing to upload footage to external servers. These drones are already being used to monitor rebar placement, concrete curing, and site activity. Their ability to perform immediate analysis means faster decision-making and better compliance with project schedules.
Drone-based layout verification and volumetric scanning, combined with 3D BIM models, is rapidly replacing manual surveying. This enables real-time site updates and faster clash detection, especially in complex concrete and steel structures.
Digital Twins + BIM2RDT: Real-Time Construction Intelligence
Digital Twins in construction are virtual replicas of physical assets updated in real time using data from sensors, cameras, and field devices. When combined with BIM2RDT (Real-time Data Transfer) systems, they deliver a new level of visibility and decision-making.
The BIM2RDT framework, developed as an agentic AI safety-first approach, transforms static BIM models into dynamic, robot-ready digital twins. It integrates data from BIM geometry, IoT sensors, and robot-collected visual-spatial data, enabling autonomous field operations and enhancing jobsite intelligence.
Semantic-Gravity ICP (SG-ICP), a cutting-edge registration method used in this framework, uses large language models to align real-time point clouds with BIM semantics. This improves alignment accuracy and avoids misinterpretation of critical site elements.
HAV (Hand-Arm Vibration) monitoring and real-time IFC-mapped safety alerts are also part of this framework, reinforcing safety and compliance.
With Digital Twins and BIM2RDT, construction teams can track progress, detect misalignments, and make timely decisions that reduce cost, enhance safety, and support project delivery.
Robotics in Masonry and Structural Work
Construction robotics are evolving fast. No longer confined to factories, robots are appearing on active sites for masonry, welding, layout, and rebar assembly.
Robotics in construction include:
- Autonomous heavy equipment for excavation
- Cobots for cutting, welding, and lifting
- Layout robots for accurate site preparation
Robots also improve safety by reducing exposure to hazardous tasks, handling repetitive work, and operating in confined or dangerous environments.
The construction robotics market is expected to reach $3.6 billion by 2030, and 2026 will mark its mainstream entry.
3D Printing for Structural Elements
3D printing in construction is accelerating. By 2026, multi-story buildings will be printed in less than 48 hours, thanks to new concrete formulations and faster print heads.
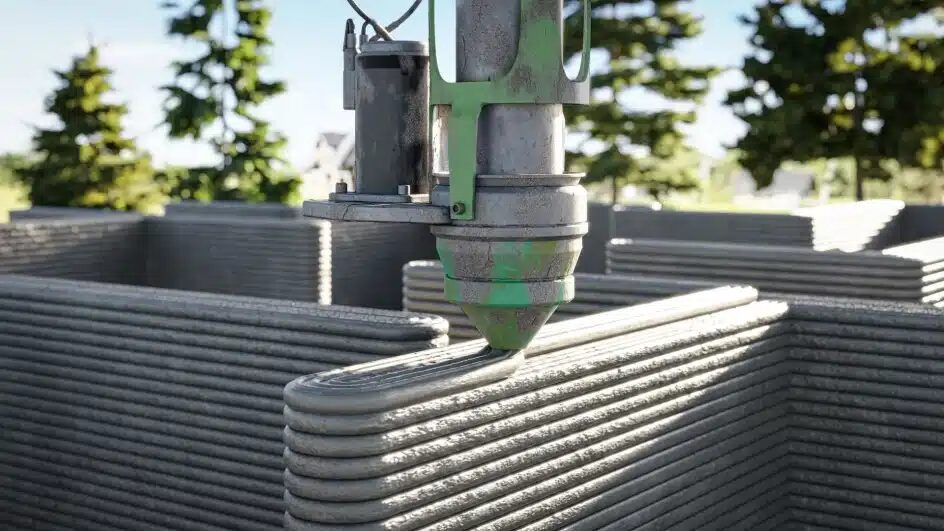

With a projected CAGR of over 100% between 2025 and 2030, 3D printing is a serious player in commercial and structural construction.
For rebar detailing, this means planning reinforcement layouts compatible with printing paths. Innovations in printing allow for embedded mesh or robotic integration of bars.
Tools like Allplan and Revit are being enhanced to simulate printed layers and automate reinforcement paths.
Sustainability Through Rebar Optimization
As the industry moves toward decarbonization, optimizing rebar usage has become a key strategy. Rebar accounts for up to 60% of the carbon emissions in reinforced concrete structures.
New strategies like special-length-priority optimization and mechanical couplers are emerging to reduce rebar waste and embodied carbon. Studies show these methods can cut rebar consumption by over 25% and carbon emissions by up to 95%.
Lap splice elimination, coupled with coupler integration, minimizes cutting waste and enhances structural efficiency. These strategies align with global sustainability targets like COP28 and the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
The Role of BIM and Rebar Detailing Software
Across all these innovations, one thing remains consistent: the reliance on high-quality 3D modeling and detailing software. Tools like AutoCAD, Revit, Allplan, and Tekla Structures are the backbone of digital construction workflows.
Rebar detailers must produce accurate drawings that not only reflect structural intent but also support fabrication and installation. With AI-powered plugins and automation features, many platforms can now assist in generating reinforcement data including bar bending schedules, clash detection, and optimized rebar placement paths, significantly reducing manual drafting time and improving overall detailing accuracy.
5D BIM models, incorporating cost and time dimensions, are also on the rise, offering real-time visualizations of how design changes impact budget and scheduling.
This shift requires a new skillset. Detailing professionals must be fluent in parametric modeling, understand construction sequencing, and collaborate in real time through cloud platforms like BIM 360. The result is a more connected, responsive design process that reduces waste, avoids errors, and accelerates construction timelines.
Conclusion: What Lies Ahead
By 2026, the construction industry will be smarter, faster, and more efficient. The integration of modular construction, AI-driven tools, robotics, digital twins, and BIM in construction is no longer optional, it’s inevitable.
For rebar detailers, structural engineers, and BIM professionals, adapting to these changes means embracing new technologies, upskilling in advanced modeling tools, and understanding how digital workflows intersect with real-world site conditions.
Contractors who adopt smart construction technologies today will gain speed, quality, and sustainability advantages tomorrow. Those who delay adoption risk obsolescence in an increasingly digitized and regulated industry.
The future of construction isn’t just digital – it’s intelligent, automated, and data-driven. And it’s already underway.
FAQ
- What is BIM in construction?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital process that creates and manages 3D models for construction projects. It enhances coordination, reduces errors, and enables real-time collaboration among architects, engineers, and contractors. - How does AI impact construction in 2026?
AI in construction automates tasks like drawing analysis, material logistics, and risk prediction. It improves decision-making, speeds up planning, and reduces labor dependency. - What are Digital Twins and how are they used?
Digital Twins are real-time digital replicas of physical structures. In 2026, they are integrated with BIM and IoT sensors to monitor construction progress, detect issues, and support autonomous systems. - Is 3D printing viable for structural elements?
Yes, 3D printing is now used for load-bearing walls and entire buildings. With embedded reinforcement and faster curing, it’s becoming a standard method for prefab structures. - How can rebar detailing be optimized for sustainability?
Using mechanical couplers, special-length strategies, and AI-driven scheduling can reduce rebar waste and carbon footprint. This aligns with global climate goals and improves project efficiency.

